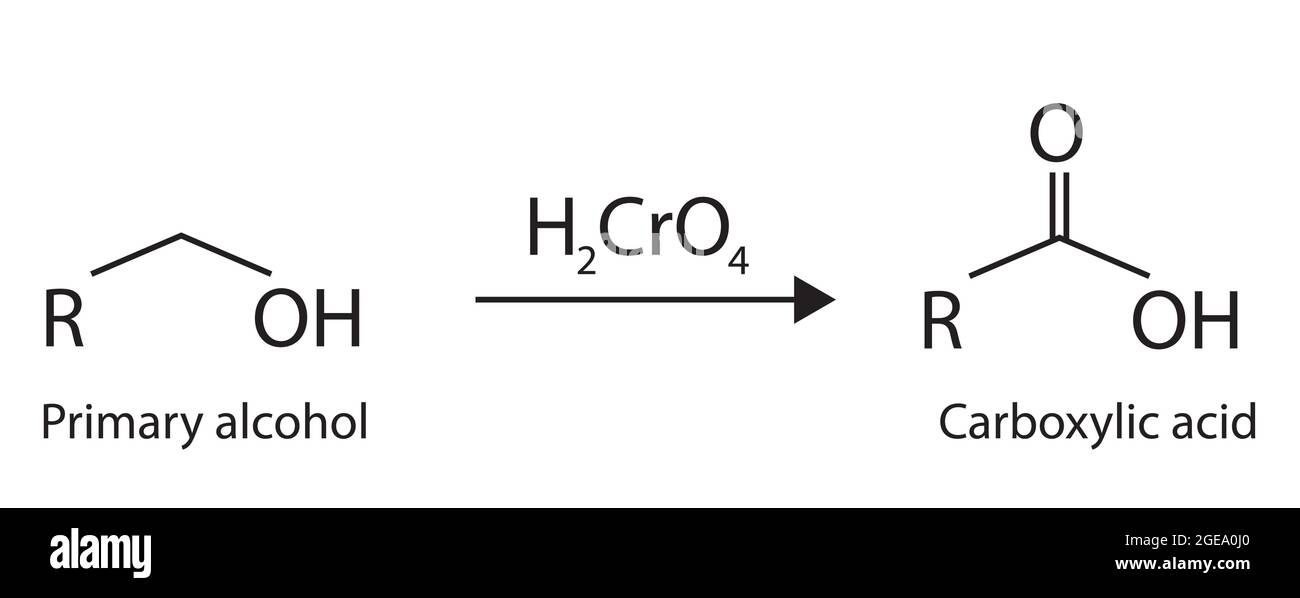
An Aldehyde Forms A Carboxylic Acid By - Under acidic conditions, the aldehyde is oxidised to a carboxylic acid. Aldehydes have a proton attached to the carbonyl carbon which can be abstracted,. An aldehyde can be oxidized to a carboxylic acid by the addition of an oxygen. Aldehydes can be oxidized to carboxylic acids with a variety of oxidizing agents such as.
Aldehydes have a proton attached to the carbonyl carbon which can be abstracted,. Aldehydes can be oxidized to carboxylic acids with a variety of oxidizing agents such as. An aldehyde can be oxidized to a carboxylic acid by the addition of an oxygen. Under acidic conditions, the aldehyde is oxidised to a carboxylic acid.
Aldehydes have a proton attached to the carbonyl carbon which can be abstracted,. Under acidic conditions, the aldehyde is oxidised to a carboxylic acid. An aldehyde can be oxidized to a carboxylic acid by the addition of an oxygen. Aldehydes can be oxidized to carboxylic acids with a variety of oxidizing agents such as.
Chemical Structure of carboxylic acid formation from aldehyde
An aldehyde can be oxidized to a carboxylic acid by the addition of an oxygen. Under acidic conditions, the aldehyde is oxidised to a carboxylic acid. Aldehydes can be oxidized to carboxylic acids with a variety of oxidizing agents such as. Aldehydes have a proton attached to the carbonyl carbon which can be abstracted,.
Carboxylic Acid To Aldehyde Dibal cloudshareinfo
Aldehydes can be oxidized to carboxylic acids with a variety of oxidizing agents such as. Under acidic conditions, the aldehyde is oxidised to a carboxylic acid. An aldehyde can be oxidized to a carboxylic acid by the addition of an oxygen. Aldehydes have a proton attached to the carbonyl carbon which can be abstracted,.
How do you make Aldehyde from Carboxylic acid?
An aldehyde can be oxidized to a carboxylic acid by the addition of an oxygen. Under acidic conditions, the aldehyde is oxidised to a carboxylic acid. Aldehydes can be oxidized to carboxylic acids with a variety of oxidizing agents such as. Aldehydes have a proton attached to the carbonyl carbon which can be abstracted,.
Structures of Carboxylic Acid Derivatives Concept Organic Chemistry
Aldehydes have a proton attached to the carbonyl carbon which can be abstracted,. Aldehydes can be oxidized to carboxylic acids with a variety of oxidizing agents such as. Under acidic conditions, the aldehyde is oxidised to a carboxylic acid. An aldehyde can be oxidized to a carboxylic acid by the addition of an oxygen.
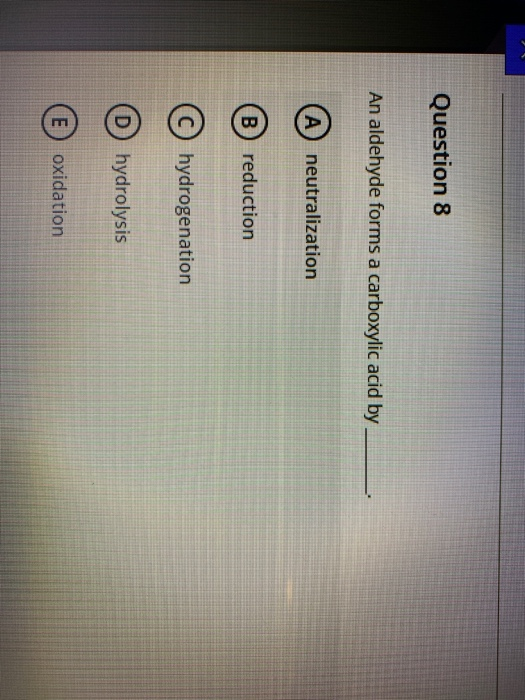
Solved Question 8 An aldehyde forms a carboxylic acid by A
Aldehydes have a proton attached to the carbonyl carbon which can be abstracted,. Under acidic conditions, the aldehyde is oxidised to a carboxylic acid. An aldehyde can be oxidized to a carboxylic acid by the addition of an oxygen. Aldehydes can be oxidized to carboxylic acids with a variety of oxidizing agents such as.
Aldehyde To Carboxylic Acid
Under acidic conditions, the aldehyde is oxidised to a carboxylic acid. An aldehyde can be oxidized to a carboxylic acid by the addition of an oxygen. Aldehydes have a proton attached to the carbonyl carbon which can be abstracted,. Aldehydes can be oxidized to carboxylic acids with a variety of oxidizing agents such as.
Alcohol To Carboxylic Acid / Carboxylic Acids MCATAid / When a
Aldehydes have a proton attached to the carbonyl carbon which can be abstracted,. An aldehyde can be oxidized to a carboxylic acid by the addition of an oxygen. Under acidic conditions, the aldehyde is oxidised to a carboxylic acid. Aldehydes can be oxidized to carboxylic acids with a variety of oxidizing agents such as.
Carboxylic Acid To Aldehyde cloudshareinfo
Aldehydes have a proton attached to the carbonyl carbon which can be abstracted,. Aldehydes can be oxidized to carboxylic acids with a variety of oxidizing agents such as. An aldehyde can be oxidized to a carboxylic acid by the addition of an oxygen. Under acidic conditions, the aldehyde is oxidised to a carboxylic acid.
Carboxylic Acid To Aldehyde Mechanism cloudshareinfo
Aldehydes have a proton attached to the carbonyl carbon which can be abstracted,. Under acidic conditions, the aldehyde is oxidised to a carboxylic acid. Aldehydes can be oxidized to carboxylic acids with a variety of oxidizing agents such as. An aldehyde can be oxidized to a carboxylic acid by the addition of an oxygen.
Aldehydes Ketones and Carboxylic Acids PDF Carboxylic Acid Ketone
An aldehyde can be oxidized to a carboxylic acid by the addition of an oxygen. Aldehydes have a proton attached to the carbonyl carbon which can be abstracted,. Under acidic conditions, the aldehyde is oxidised to a carboxylic acid. Aldehydes can be oxidized to carboxylic acids with a variety of oxidizing agents such as.
Under Acidic Conditions, The Aldehyde Is Oxidised To A Carboxylic Acid.
Aldehydes have a proton attached to the carbonyl carbon which can be abstracted,. An aldehyde can be oxidized to a carboxylic acid by the addition of an oxygen. Aldehydes can be oxidized to carboxylic acids with a variety of oxidizing agents such as.