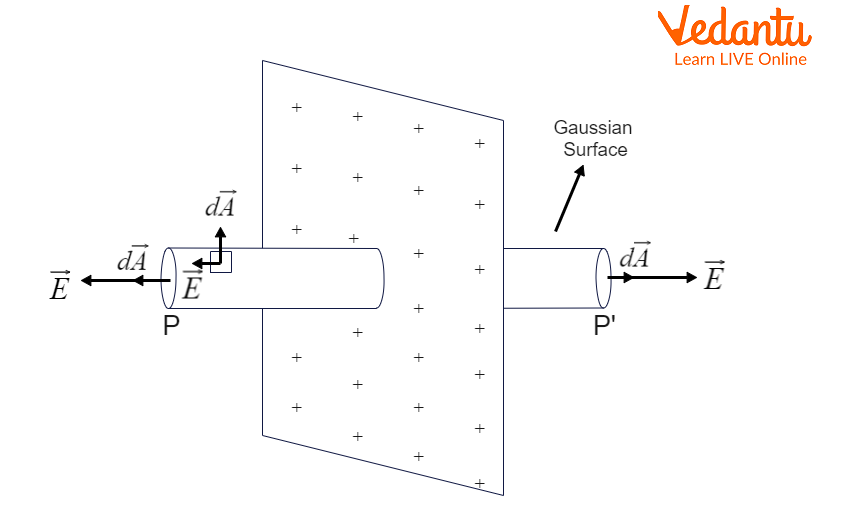
Electric Field For Infinite Sheet - (1.6.12) (1.6.12) e = σ 2 ϵ 0. Use gauss’s law to find the electric field caused by a thin, flat, infinite sheet with a uniform positive surface charge density $\sigma$. Using gauss’s law, prove that the electric field at a point due to a uniformly charged infinite plane sheet is independent of the. All we have to do is to put α = π/2 α = π / 2 in equation 1.6.10 to obtain. Therefore only the ends of a cylindrical gaussian surface. For an infinite sheet of charge, the electric field will be perpendicular to the surface. This is independent of the.
Using gauss’s law, prove that the electric field at a point due to a uniformly charged infinite plane sheet is independent of the. For an infinite sheet of charge, the electric field will be perpendicular to the surface. All we have to do is to put α = π/2 α = π / 2 in equation 1.6.10 to obtain. (1.6.12) (1.6.12) e = σ 2 ϵ 0. Therefore only the ends of a cylindrical gaussian surface. This is independent of the. Use gauss’s law to find the electric field caused by a thin, flat, infinite sheet with a uniform positive surface charge density $\sigma$.
Using gauss’s law, prove that the electric field at a point due to a uniformly charged infinite plane sheet is independent of the. (1.6.12) (1.6.12) e = σ 2 ϵ 0. Therefore only the ends of a cylindrical gaussian surface. This is independent of the. For an infinite sheet of charge, the electric field will be perpendicular to the surface. Use gauss’s law to find the electric field caused by a thin, flat, infinite sheet with a uniform positive surface charge density $\sigma$. All we have to do is to put α = π/2 α = π / 2 in equation 1.6.10 to obtain.
Electric field intensity due to a thin infinite plane sheet of charge
Therefore only the ends of a cylindrical gaussian surface. All we have to do is to put α = π/2 α = π / 2 in equation 1.6.10 to obtain. This is independent of the. Use gauss’s law to find the electric field caused by a thin, flat, infinite sheet with a uniform positive surface charge density $\sigma$. For an.
electrostatics Electric field due to uniformly charged infinite plane
Use gauss’s law to find the electric field caused by a thin, flat, infinite sheet with a uniform positive surface charge density $\sigma$. Using gauss’s law, prove that the electric field at a point due to a uniformly charged infinite plane sheet is independent of the. (1.6.12) (1.6.12) e = σ 2 ϵ 0. For an infinite sheet of charge,.
homework and exercises Electric field of an infinite sheet of charge
For an infinite sheet of charge, the electric field will be perpendicular to the surface. This is independent of the. (1.6.12) (1.6.12) e = σ 2 ϵ 0. Therefore only the ends of a cylindrical gaussian surface. All we have to do is to put α = π/2 α = π / 2 in equation 1.6.10 to obtain.
homework and exercises Find the electric field of an infinite sheet
All we have to do is to put α = π/2 α = π / 2 in equation 1.6.10 to obtain. This is independent of the. Use gauss’s law to find the electric field caused by a thin, flat, infinite sheet with a uniform positive surface charge density $\sigma$. For an infinite sheet of charge, the electric field will be.
SOLUTION 3 electric field infinite sheet Studypool
Using gauss’s law, prove that the electric field at a point due to a uniformly charged infinite plane sheet is independent of the. Therefore only the ends of a cylindrical gaussian surface. For an infinite sheet of charge, the electric field will be perpendicular to the surface. All we have to do is to put α = π/2 α =.
electrostatics Electric field due to uniformly charged infinite plane
This is independent of the. For an infinite sheet of charge, the electric field will be perpendicular to the surface. (1.6.12) (1.6.12) e = σ 2 ϵ 0. Using gauss’s law, prove that the electric field at a point due to a uniformly charged infinite plane sheet is independent of the. Use gauss’s law to find the electric field caused.
Electric Field due to Infinite Plane Important Concepts for JEE
This is independent of the. Therefore only the ends of a cylindrical gaussian surface. All we have to do is to put α = π/2 α = π / 2 in equation 1.6.10 to obtain. Using gauss’s law, prove that the electric field at a point due to a uniformly charged infinite plane sheet is independent of the. (1.6.12) (1.6.12).
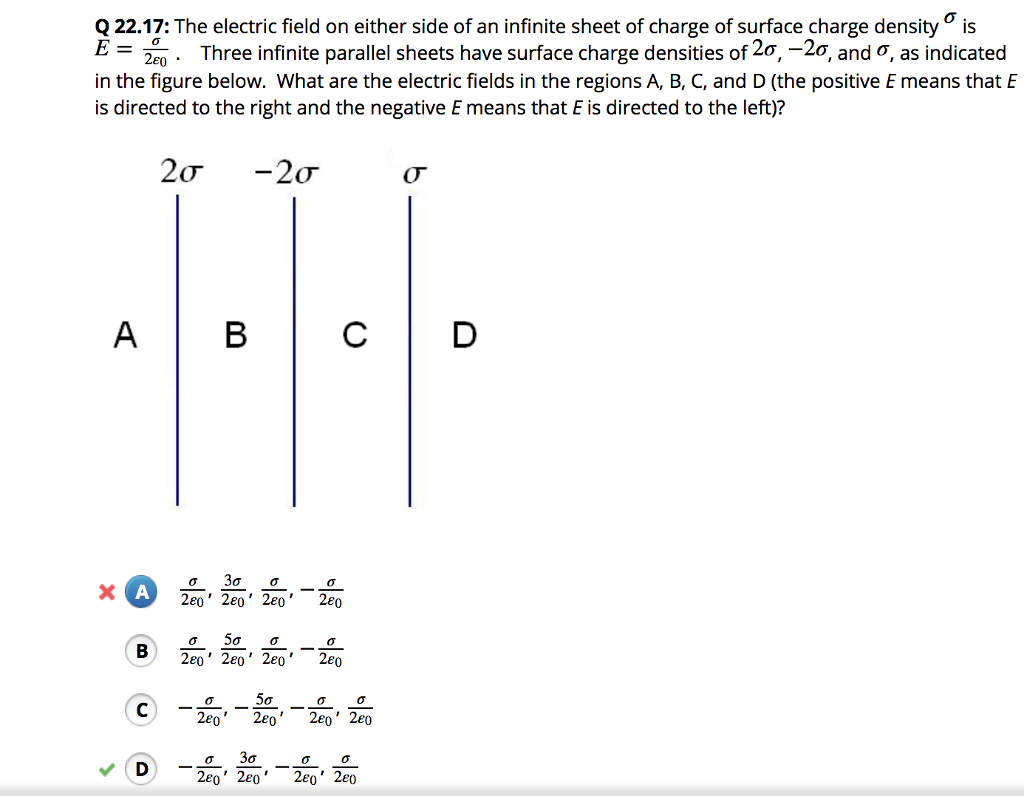
Solved The electric field on either side of an infinite
Use gauss’s law to find the electric field caused by a thin, flat, infinite sheet with a uniform positive surface charge density $\sigma$. Therefore only the ends of a cylindrical gaussian surface. For an infinite sheet of charge, the electric field will be perpendicular to the surface. (1.6.12) (1.6.12) e = σ 2 ϵ 0. All we have to do.
Electric field due to infinite non conducting sheet of surface charge
Use gauss’s law to find the electric field caused by a thin, flat, infinite sheet with a uniform positive surface charge density $\sigma$. All we have to do is to put α = π/2 α = π / 2 in equation 1.6.10 to obtain. Therefore only the ends of a cylindrical gaussian surface. This is independent of the. (1.6.12) (1.6.12).
SOLUTION 3 electric field infinite sheet Studypool
(1.6.12) (1.6.12) e = σ 2 ϵ 0. All we have to do is to put α = π/2 α = π / 2 in equation 1.6.10 to obtain. Use gauss’s law to find the electric field caused by a thin, flat, infinite sheet with a uniform positive surface charge density $\sigma$. Using gauss’s law, prove that the electric field.
(1.6.12) (1.6.12) E = Σ 2 Ε 0.
All we have to do is to put α = π/2 α = π / 2 in equation 1.6.10 to obtain. This is independent of the. For an infinite sheet of charge, the electric field will be perpendicular to the surface. Use gauss’s law to find the electric field caused by a thin, flat, infinite sheet with a uniform positive surface charge density $\sigma$.
Using Gauss’s Law, Prove That The Electric Field At A Point Due To A Uniformly Charged Infinite Plane Sheet Is Independent Of The.
Therefore only the ends of a cylindrical gaussian surface.